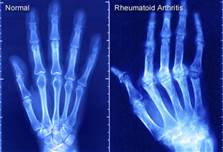
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that can cause chronic inflammation of the joints and other areas of the body.
Rheumatoid arthrities
It is the most systemic inflammatory disease characterized by symmetrical joint involvement. Extra-articular involvement, including neurologic dysfunction, eye inflammation, rheumatoid nodules, cardiopulmonary disease, lymph adenopathy and splenomegaly are the manifestations of the disease.
Pathophysiology: Chronic inflammation of the synovial tissue lining the joint capsule results in the proliferation of this tissue. The inflamed, proliferating synovial characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis is called pannus. This pannus invades the cartilage and eventually the bone surface, producing erosions of bone and cartilage and leading to destruction of the joint. Sign and Symptoms: weakness, stiffness and Joint pain, Tenderness with warmth and swelling over affected joints.
Diagnosis:
Therapy: Non-pharmacologic therapy:
Rest, physical therapy, occupational therapy, use of assistive devices, weight reduction, and surgery.
Drug therapy:
Methotrexate: It is considered as the DMARD of choice by many rheumatologists for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Methotrexate inhibits cytokine production, inhibits purine biosynthesis, and may stimulate release of adenosine, all of which may lead to its anti-inflammatory properties. The drug has a fairly rapid onset of action; results may be seen as early as 2-3 weeks after starting of the therapy. Absorption of methotrexate is variable, metabolized intracellularly to polyglutamated derivatives and is excreted by the kidneys.
Methotrexate is contraindicated in pregnant and nursing women, leucopenia, chronic liver disease, pleural or peritoneal effusions, immunodeficiency, thrombocytopenia, preexisting blood disorders, and a creatinine clearance of less than 40 mL/min.
Adverse effects: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, cirrhosis is rare.
Leflunomide: Leflunomide is a DMARD that inhibits pyrimidine synthesis, leading to a decrease in lymphocyte proliferation and modulation of inflammation.
Hydroxychloroquine: The Hydroxychloroquine is the lack of myelosuppressive, hepatic, and renal toxicities that may be seen with other DMARDs. It is well absorbed orally and widely distributed to body tissues. Hydroxychloroquine is partially metabolized in the liver and is excreted by the kidney.
Adverse effects: vomiting, nausea and diarrhea. Vertigo, headache and insomnia
Toxicities: Ocular toxicity, dermatologic toxicity.
Sulfasalazine: It a prodrug cleaved by bacteria in the colon into sulfapyridine and 5 amino salicylic acid. Sulfapyridine moiety is responsible for the anti-rheumatic properties.
Adverse effects: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and urticaria.
Other Disease-Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs: Gold salts, penicillamine, azathioprine, D- cyclosporine, cyclophosphamide and minocycline,
Biologic Agents: These are the agents prepared by genetically engineered protein molecules that block the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α (adalimumab, infliximab, etanercept,) and IL-1 (anakinra) etc. These drugs may be effective when other DMARDs fail to achieve adequate responses but are considerably more expensive to use. They have no toxicity.
Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are used in rheumatoid arthritis for their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. They interfere with antigen presentation to T lymphocytes, inhibit prostaglandin and leukotriene synthesis, and inhibit neutrophil and monocytes superoxide radical generation.
Autoimmune, swollen, painful joints